For some, it can feel unnerving to know you are being tracked by your employer while working. Images of a big eye in the sky spying on your every move makes some employees uncomfortable with using GPS time clock.
Most of these concerns are ill-founded, however, and based on misconceptions about how employee GPS time tracking works. Here’s everything you need to know to understand how GPS time tracking really works.
Download the Guide How to Introduce GPS Time Tracking to Your Mobile Workforce
What Is Employee GPS Time Tracking?
Employee tracking - or personnel tracking - allows employers to keep track of what their employees are working on at any given time. For GPS employee time tracking, managers can run smoother operations by knowing where their employees are located throughout the workday.
While some GPS systems are used to track company vehicles and/or equipment, an employee GPS time tracking solution does more than just track an employee’s location and hours worked.
It's unique to each individual worker and helps managers collect accurate time data (and more) with the employees’ mobile devices.
The History of GPS
When Russia launched Sputnik in 1957, it opened the door for today’s Global Positioning Satellites (GPS): A system we now use for everything from mapping and military to farming and science.
Since the Sputnik satellite was launched into space, more have joined to orbit the earth. In the 1960s, the U.S. Navy used satellite navigation experiments to find submarines that were carrying nuclear missiles. With only six satellites, they could locate the subs within minutes.
In the 1970s, the U.S. Department of Defense launched the first Navigation System with Timing and Ranging (NAVSTAR) satellite. NASA explains the 24-satellite system “became fully operational in 1993” and was launched to “support their proposed navigation system.”
Today, there are more than 2,600 satellites orbiting in space with the majority owned by the U.S., according to the Union of Concerned Scientists. As of this writing, of the 1,327 U.S.-owned satellites, their usage is broken down as:
- Civil: 30
- Commercial: 935
- Government: 170
- Military: 192
According to NASA, satellites wear out “just like old washing machines and vacuum cleaners” and, depending on their size and where they are in space, will either be slowed down to crash and literally burn in the earth’s atmosphere, or sent farther out into space.
How Does GPS Work?
The satellites in space orbit the earth at different distances. The satellites send different information to earth, depending on where they are orbiting.
According to experts, Low altitude satellites - termed Low Earth Orbit Satellites or LOE - have to maintain a speed of at least eight kilometers (4.97097 miles) per second to avoid crashing back down to earth. They circle the planet once about every 90 minutes because they are closer to the earth.
LOEs are used predominantly for collecting images of earth. They are invaluable for helping assess military movement, geological changes, and weather patterns, among other things.
Farther out - over 12,500 miles above ground - are the Medium Earth Orbit satellites (MEO) which orbit the earth twice per day. These are where 25 navigation satellites provide precise GPS locations as they simultaneously orbit the planet.
At any given moment, there are at least four satellites giving signals to GPS devices on the ground. When at least three satellite signals cross in space, an accurate location is pinpointed on earth.
With popular GPS software or devices, these are the satellites we use to navigate our routes.
And, finally, high-altitude satellites called Geo-stationary orbit satellites (GEO), are the farthest out - more than 22,000 miles - and orbit earth once every 24 hours. Since they take exactly 24 hours to orbit, they actually appear stationary. These satellites are used for things like weather, broadband internet services, and direct-to-home movie streaming services and they are crucial for our communication.
How Time Tracking Works
When the satellites reach space, their cameras and solar panels are activated and they communicate with signals coming from earth stations on the ground. GPS devices and systems send signals back and forth to these satellites
Since the satellites never stop orbiting, the location recorded from a mobile device is always available, as long as the device is powered on. There are many apps that use GPS tracking. For example, a weather app needs access to your location. Google helps you find a particular product or service near you.
Increasingly, companies use GPS phone tracking for sales and marketing purposes and to collect various data. Indeed, some apps contain malware or use other invasive techniques to collect and sell personal data.
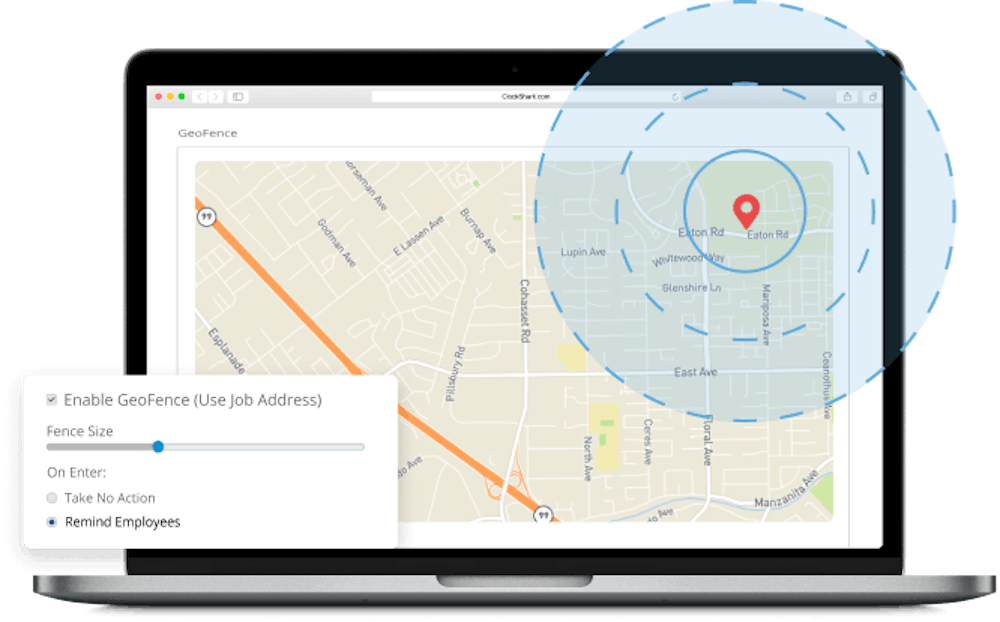
However, GPS time tracking apps for employees are not for these purposes.
When you use a mobile GPS time tracking app, your location is not known to the employer until you clock in. That is when the app is activated. Conversely, when you clock out, your location is no longer being tracked by your employer.
When employees use a GPS time tracking app, their employers can pull up an accurate, real-time location of where each worker is. With GPS time tracking, workers can also provide proof of where they were during the day with a bread crumb trail.
Conclusion
Employee GPS time tracking works with government-owned and military-used satellites above the earth. It’s not intended to be a spy tool or to monitor every move of employees all day, every day.
The benefits to employees are many. They will have an accurate record of everything they did as well as an accurate paycheck on payday that reflects the exact work they’ve done. And with GPS time tracking, their privacy is never compromised with a trusted mobile app.







